Autumn is on the threshold, which means that the annual flu vaccination will begin soon. Why get vaccinated against the flu for those who rarely get sick? Are obsessive reminders of this an advertisement for drug manufacturers? How are free vaccines different from paid vaccines? Read our material, which will always be relevant.
 129386
129386
Why should I get vaccinated against influenza? Is this an advertisement from the vaccine manufacturers?
Influenza is an acute respiratory viral infection or the well-known ARVI. It is necessary to protect yourself from the flu, because the disease is sometimes very difficult, and in some cases it can end in the death of the patient. According to the latest estimates, up to 650,000 people die each year from respiratory diseases worldwide.
Source: CDC
Even if the flu is not severe, it lasts about a week. The patient during this time is usually tormented by headaches and muscle pain, sore throat and runny nose. The cough may persist for several weeks. Thus, influenza adversely affects academic performance and performance, as patients are forced to be treated at home.
The idea that vaccinations are a way for drug companies to extract money is fundamentally wrong and has been debunked numerous times. Vaccination is a great way to save money that could be spent on treating a disease. In the case of influenza, which does not require the use of expensive drugs, the savings are mainly in the preservation of labor productivity. People do not go on sick leave and work more.
I rarely get sick, why should I get vaccinated?
Even if you rarely get sick and never experience complications from a cold, you should get vaccinated to keep flu viruses from spreading. Influenza is highly contagious, it is spread by airborne droplets through coughing, sneezing and talking, and can also be left on the hands. Ideal places for its distribution are large gatherings of people, such as a kindergarten or school.
Remember that not everyone can be vaccinated, some people cannot receive the vaccine due to contraindications, and some of them are in risk zone, that is, more likely to endure the flu heavily. At the same time, an epidemic can be prevented by creating “herd immunity”, when most of the population is vaccinated, and there is simply no one to infect the virus.
Important
In addition to vaccination, flu prevention includes: frequent handwashing, use of disposable handkerchiefs when sneezing and coughing, and social distancing. If you are sick, stay at home, and avoid crowded places during a flu epidemic.
What flu vaccines are there, why are they updated?
Vaccines protect us from influenza viruses types A and B. They are the ones that can cause epidemics, and therefore pose the greatest danger. In this case, influenza A viruses are divided into subtypes, and influenza B viruses are divided into lines. For this reason, influenza vaccines are always composite, they contain several types (strains) of viruses at once. To obtain modern vaccines, viruses are either inactivated (killed) or only parts of them necessary to develop immunity against infection are used. Vaccines with live, attenuated viruses are rarely used.
In addition to the fact that several strains of influenza viruses always circulate in the world at once, every year they are updated, slightly changing their genome so that our immune system does not recognize them. So every year people need new vaccines to protect themselves.
In order to track the spread of viruses and identify new strains, the World Health Organization has created the Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System, in which experts around the world monitor which viruses and where they circulate.
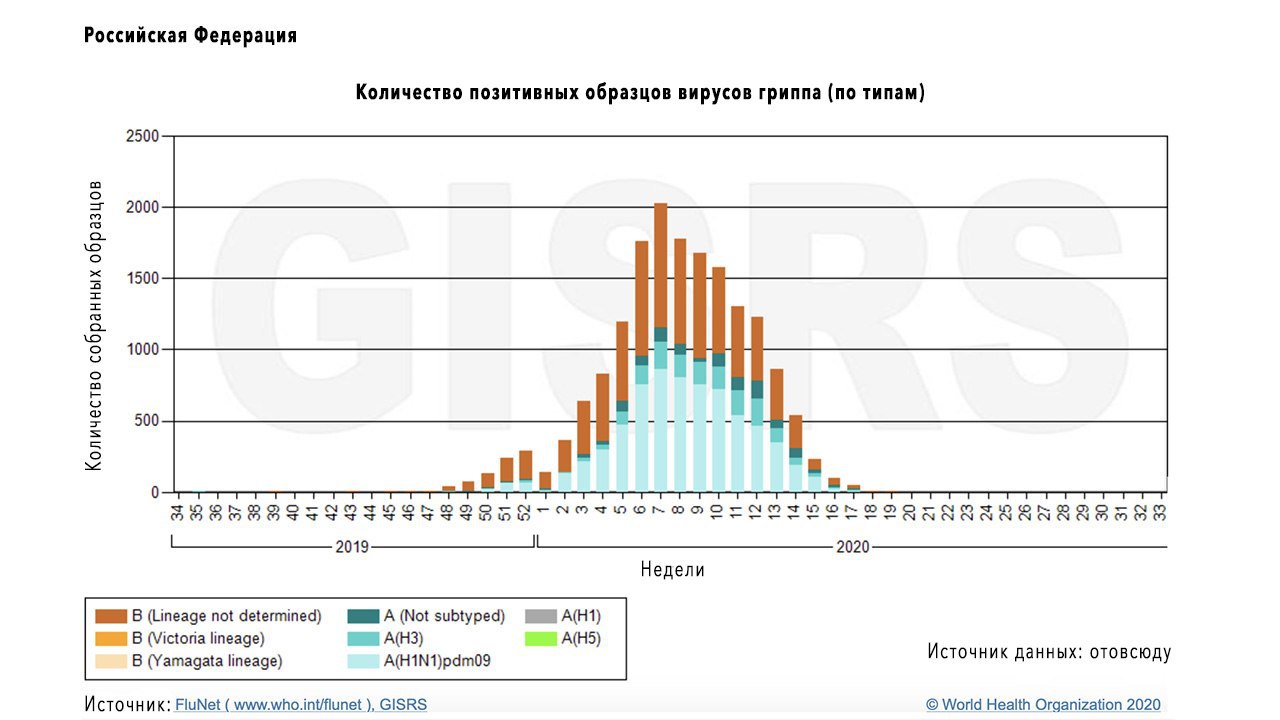
Figure 1. Number of samples of different strains of influenza A and B viruses collected in Russia in 2019-2020 Source
Based on the data obtained, each country chooses which vaccines to use.
Why are there free and paid vaccines? It turns out that the paid ones are better? So free is bad?
Because flu vaccination is a public health concern, most countries offer free flu shots. Russia is no exception, the flu vaccine is included in the Russian National Immunization Schedule. Usually, only one vaccine selected for a large vaccination campaign is vaccinated free of charge, other vaccines can be obtained for a fee.
A free vaccine is not always worse than a paid one, the main thing is to understand how one drug differs from another. Before getting vaccinated, check with your doctor about which vaccines are available and which are preferred. Some of them can only protect against three strains of the virus, others – from four strains. Live vaccines may be more effective but are more likely to cause side effects. When choosing an inactivated vaccine, which contains individual viral antigens (for example, hemagglutinin and neuraminidase), pay attention to their number. A vaccine is considered to be highly effective if it contains at least 15 micrograms of hemagglutinin of each virus strain per vaccine dose.
Important < p>Do not forget that the composition of influenza vaccines changes every year, and the effectiveness of the drugs depends largely on whether epidemiologists were able to guess which strains of viruses would infect people in a particular region. If you got the vaccine last year and still got sick, it does not mean that it is useless to get vaccinated against the flu.
Will the vaccine make my immune system weaker, because the body itself must resist?
Vaccination does not weaken the immune system, but trains it, making it stronger. Influenza vaccines most often contain killed viruses or only parts of them (antigens) – a kind of “imprints” of the causative agent of the disease. The vaccine itself is not capable of causing an infection, but it allows the immune system to remember the antigens of influenza viruses and, upon encountering a wild pathogen, quickly exterminate the enemy.
What complications can the flu vaccine cause?
Inactivated influenza vaccines are generally well tolerated. Common side effects after them include: redness, swelling and pain at the injection site. Live vaccines containing attenuated virus strains (given intranasally) can cause mild cold symptoms such as a short cough, mild fever, malaise, and joint pain. Such drugs are intended for people from 2 to 49 years old and are not used to vaccinate pregnant women.
Severe complications from influenza vaccination, such as allergic reactions, are extremely rare. In order to eliminate the risk of such complications, stay in the clinic's waiting room for 30 minutes after the vaccine is administered.
Important
A frequent contraindication to influenza vaccination is an allergy to chicken egg protein (influenza vaccine viruses are grown on chicken embryos), but in practice, allergy sufferers are successfully vaccinated. Influenza vaccines are purified from foreign proteins and are recognized as safe even for people with an anaphylactic reaction to chicken protein. You should not be vaccinated only in case of negative reactions to past doses of the drug.
Should children be vaccinated? And the elderly?
Children under 5 and the elderly are at risk for influenza, along with pregnant women, immunosuppressed people, and people with chronic illnesses. This means that their disease is more likely to be severe and can be fatal. In developed countries, most influenza deaths occur in people over the age of 65. People in risk groups should be vaccinated first. Getting flu vaccines is also important:
-
schoolchildren and students,
-
health care workers , teachers, transport workers and public utilities,
-
conscripts for military service.
All of them spend most of their lives in close groups, which means they are most susceptible to infection with the flu.
