Most medical interventions in the maxillofacial area are accompanied by pain sensations of varying degrees of intensity, so high-quality anesthesia during their implementation is an urgent problem in dentistry. Improving dental care for the population is impossible without the introduction of effective modern anesthetics into everyday practice. To date, the interchangeability of drugs is one of the most serious debatable issues both in Russia and around the world. According to experts, the production of generics is the most important and leading strategic direction in the development of the pharmaceutical industry, which will continue in the next decade.

An original drug is a new drug synthesized for the first time and completed a full cycle of research, the active ingredients of which are protected by a patent for a certain period, and significant intellectual and material resources have been spent on development, clinical trials, production and market introduction. Generic is a generic drug, similar to the patented (original) drug and brought to the market after the expiration of the patent protection of the original.
The algorithm for the production of generic and original pharmaceutical products is the same and complies with the requirements of WHO, which regulate strict standards for premises, equipment, raw materials, personnel, quality control methods, etc. However, the procedure for registering generics is much cheaper and takes less time, as it does not require a full cycle of clinical trials.
Currently, the domestic dental market has a sufficient number of original drugs and generics of the articaine series. Brilocaine is a combined drug for local anesthesia in dentistry.
Indications for use:infiltration and conduction anesthesia, including in patients with concomitant somatic pathology.
Contraindications for use:
- hypersensitivity to articaine, adrenaline, sulfites, auxiliary components of the drug;
- bronchial asthma with increased sensitivity to sulfites;
- porphyria, hyperthyroidism, angle-closure glaucoma, paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, simultaneous use of non-selective b-blockers.
The purpose of the study
To evaluate the effectiveness Brilocaine anesthetic at a dental appointment.
Materials and methods
In January-March 2015, 22 dentists were interviewed. All of them are employees of municipal dental clinics in Volgograd. To assess the effectiveness of anesthesia, subjective and objective indicators characterizing the intensity of pain in a patient were studied. For this, visual analogue scales were used, which are widely used in clinical practice. Each time after the application of Brilokain anesthetic, dentists evaluated the quality of work with it.
Results and discussion
The majority of manipulations carried out with the use of Brilocaine anesthetic was dental treatment – 55.2%. Dentists also used the drug for extraction of teeth under infiltration and conduction anesthesia (22.6% and 9.5%, respectively), preparation of teeth for artificial crowns under infiltration anesthesia (13.5%), operations on the soft tissues of the maxillary fossa and interventions on the oral mucosa. At the same time, 84.4% of respondents rated the analgesic activity of the anesthetic as high (the onset of anesthesia from the moment of administration is 1-3 minutes, high-quality anesthesia throughout the intervention), 9.3% of respondents considered the activity of Brilocaine to be medium (slower achievement of the anesthetic effect by compared with other anesthetics of the articaine series). And only in every 16th case of the use of Brilocaine anesthesia came slowly, the first injection was not enough (6.2%).
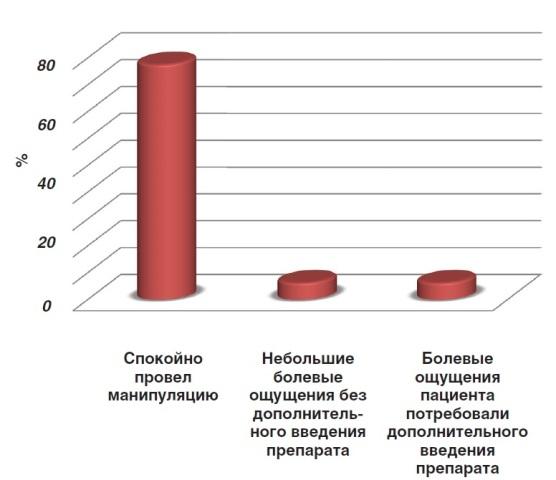
The majority of doctors (87.5%) calmly performed the manipulation, in 6.2% of cases the patient experienced slight pain during treatment, but no additional administration of the drug was required. Also, 6.2% of dentists reported that the patient experienced pain during treatment, and additional administration of the drug was required (Fig. 1). Assessing what exactly could affect the weak anesthetic activity of Brilocaine, the respondents noted the neglect of the inflammatory process, accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition of the body and the individual characteristics of the emotional sphere of patients who were anxious before starting treatment.
Fig 1. The effectiveness of the manipulation with the use of anesthetic “Brilocaine”
When choosing medicines, the majority of dentists preferred original drugs (82.4%), 12.5% did not see a difference, and only 5.1% of respondents chose generics, which speaks of doctors' distrust of domestically produced drugs.
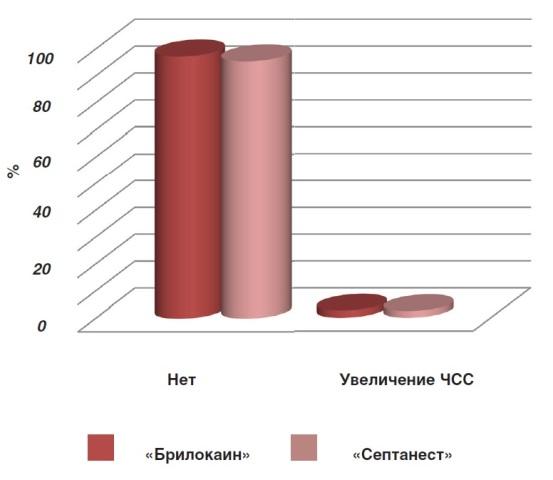
Of the adverse reactions accompanying the administration of the anesthetic Brilocaine, 2.7% of the respondents noted an increase in heart rate (Fig. 2), which is comparable with the data of I.V. Fomichev, obtained during the study of the drug Septanest in 2014. All the doctors who took part in the survey denied the occurrence of any technical difficulties during anesthesia.
Fig 2. Adverse reaction during or after the use of Brilocaine »
In the manufacture of injection solutions, all manufacturers take measures to ensure the safety of medicinal substances, use preservatives and stabilizers of the active substance: EDTA, HCl solution, glycine, etc. EDTA is a complexing agent that captures metal ions (Al, Pb) leached from glass, and removes from the body. There is an assumption that the presence of EDTA in the composition of the anesthetic can cause headache, nausea, vomiting, local tissue irritation, kidney damage, and heart rhythm disturbance. Allergic reactions to EDTA have also been described with topical corticosteroids. Confirmation or refutation of these statements is not required, since Brilokain does not include EDTA, HCl and glycine. Trilon B (EDTA disodium salt) and chemically resistant glass are used in the preparation. Possible side reactions are also reduced by the absence of parabens in Brilocaine.
Conclusions
Analysis of the results showed that in all cases of Brilocaine use, the drug was well tolerated, high-quality anesthesia was achieved with conduction and infiltration anesthesia. The absence of a number of potentially allergenic components in the composition of the anesthetic makes it possible to reduce the risk of adverse reactions during anesthesia at an outpatient dental appointment. Generic Brilocaine has all the properties of the original drug. The obtained data turned out to be comparable with the results of clinical trials of Brilocaine anesthetic and similar articaine-containing preparations conducted at Moscow State Medical University. A comparative study of the effectiveness of anesthesia and the safety of the anesthetic Brilocaine-adrenaline forte 1:100000 suggests that in the outpatient treatment of dental diseases, it has clinical and physiological parameters similar to similar articaine-containing drugs.
This is a digest of an article by Volgograd researchers:
Head physician А.V. Mikhalchenko, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Associate Professor D.V. Mikhalchenko, MD, Head of the Department
Assistant V.N. Naumova, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Dentist E.A. Filyuk
